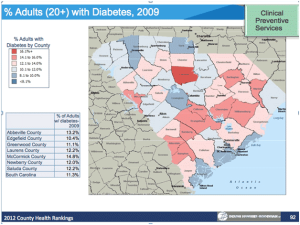
Diabetes in the Lakelands Region
Abbeville County 13.2%
Edgefield County 10.4%
Greenwood County 11.1%
Laurens County 12.2%
McCormick County 14.8%
Newberry County 12.0%
Saluda County 12.2%
South Carolina 11.3%
Types of Diabetes:
There are three types of diabetes:
- Type I: Often referred to as “juvenile diabetes,” Type I often occurs in children and adults younger than 30. However, Type I can appear at any age. Individuals with Type I produce little or no insulin and will need insulin injections as part of treatment. Ten percent or less of diabetes is Type I.
- Type II: Develops most frequently in adults who may have a family history of diabetes or who have risk factors. Type II diabetics produce insulin but the body does not use it effectively. Type II diabetes can be controlled by diet, exercise and monitoring glucose levels. It may also require pills or insulin. About 90 percent of all diabetes is Type II.
- Gestational: Occurs during pregnancy and usually disappears after pregnancy is over. Women who have diabetes during pregnancy have an elevated risk of developing Type II diabetes later in life.
Read Facing Diabetes: Local Man Shares His Journey from our news archive.
Risk Factors for Diabetes:
Risk for developing diabetes increases if:
- You have a family history (parent, grandparent, brother or sister who has diabetes).
- You are 20 percent or more above your ideal weight.
- You are older than 40.
- You are Native American, African American, Asian American or Hispanic.
- You have had gestational diabetes while pregnant.
Diabetes Prevention:
Diabetes, even for those who have been identified as having “pre diabetes,” can sometimes be prevented through lifestyle modification, including:
- Keeping your weight within a normal range.
- Lose weight if you are more than 20 percent over your ideal weight/BMI.
- Exercise to control weight and help your body use insulin more effectively.
- Get regular health checkups, including glucose testing.
Symptoms of Diabetes:
A physician or healthcare provider should diagnose diabetes, but these are some symptoms to be aware of:
- Frequent urination (especially at night)
- Feeling tired
- Unusual thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurred Vision
- Slow healing cuts, sores or infections
- Feeling hungry most of the time
- Dry, itchy skin
Diabetes Management:
Many of the same tips to manage diabetes apply to preventing diabetes, including:
- Keeping your weight within a normal range.
- Lose weight if you are more than 20 percent over your ideal weight/BMI.
- Eat a nutritious, balanced, low-fat diet to regulate glucose levels and help maintain an ideal weight.
- Exercise to control weight and help your body use insulin more effectively.
Individuals with diabetes should also:
- Monitor your glucose levels to ensure your blood sugar doesn’t go too high or low.
- Take medication or insulin as needed.
- Seek regular health care, including food and eye exams.
Diabetes can cause a tremendous amount of damage to an individual’s body, including:
- Heart Disease and Stroke
- High Blood Pressure
- Blindness
- Kidney Disease
- Neuropathy (nervous system damage)
- Amputation
- Death
Resources Available From Self Regional Healthcare:
Community Classes: Free community classes are offered on a monthly basis and are facilitated by Certified Diabetes Educators (CDEs). Each month features a different topic, with an afternoon and evening class time offered. To receive more information, call Diabetes Education at (864) 725-5007.
Screenings: Through the Self Regional Health Express, health screenings are offered around the Lakelands region, including diabetes screenings. To receive more information, call Prevention and Wellness at (864) 725-4164.
Speaker for Your Organization: Certified Diabetes Educators are available to visit your group to discuss diabetes prevention and management. To check the availability of a speaker for your group, call Diabetes Education at (864) 725-5007.
Consultations: Individuals may schedule one-on-one consultations with a certified diabetes educator, which is a healthcare service that may be covered by health insurance. To learn more, call Diabetes Education at (864) 725-5007.
Diabetes in the Lakelands Region:
| Abbeville County | 13.2% |
| Edgefield County | 10.4% |
| Greenwood County | 11.1% |
| Laurens County | 12.2% |
| McCormick County | 14.8% |
| Newberry County | 12.0% |
| Saluda County | 12.2% |
| South Carolina | 11.3% |
Updated 11-14-2013.
